Blood is responsible for delivering nutrients and oxygen to the lung and
tissues of the body. It also plays an important role in immunity. One of the
most important cells found in blood is red blood cells which contain a protein
known as hemoglobin. This is what gives blood its signature red color.
اضافة اعلان
The main role of
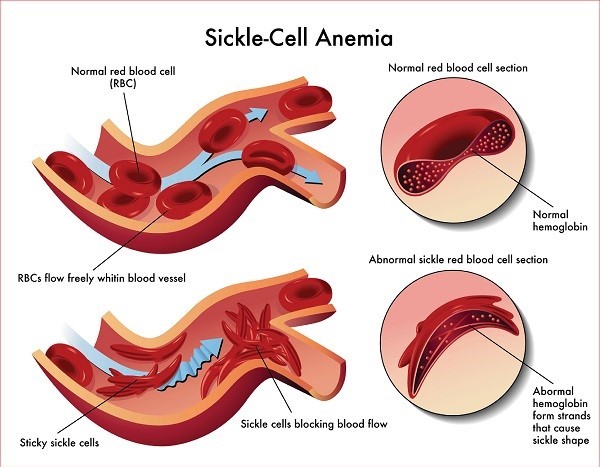
red blood cells is delivering oxygen to tissues and removing the waste, which
is later exhaled as carbon dioxide. Red blood cells are normally round,
flexible, and disk-shaped, which is important to solubilize gases properly.
In sickle cell
disease, the shape of red blood cells changes dramatically as it will no longer
be a disk shape but instead take on a rigid form in the shape of a C.
And any condition
that affects red blood cells can greatly impact overall health.
Sickle cell
disease is an inherited blood disorder directly linked to certain gene
mutations. There are different types of sickle cell disease, but all result in
a structural deformity of hemoglobin.
To have sickle
cell disease, an individual must have inherited mutated genes from both
parents. This is because this particular mutation is autosomal recessive,
meaning that the disease does not present unless both genes are inherited.
Depending on the
severity of the disease, a person can develop sickle cell anemia. If a person
only has one gene, they are considered a carrier for the disease, often
referred to as sickle cell trait.
Since carriers
typically present with no or minimal symptoms, it is difficult to estimate the
prevalence of sickle cell trait patients. However, since sickle cell disease is
more observable, the prevalence of this disease is more established.
To have sickle cell disease, an individual must have inherited mutated genes from both parents.
Globally, it is
currently estimated that 300 million people have the sickle cell trait, and 6.4
million live with sickle cell disease. This gives sickle cell disease a
prevalence rate of slightly under 0.1 percent.
Jordan has a
relatively high prevalence rate. According to a 2021 study conducted in the
Kingdom, the prevalence rate is expected to be 0.7 percent, although many
earlier studies in Jordan place the prevalence rate between 0.44 to 6 percent.
Gene mutations
Different gene mutations in various combinations can cause sickle cell
disease. These different types typically affect prognosis and manifestation of
symptoms. There are four major types of sickle cell disease, and each refers to
an inherited gene.
Hemoglobin SS
disease is the most common form of sickle cell disease and is often considered
the most severe form, with the worst symptoms at a higher rate. In this form,
the individual inherited two hemoglobin S genes.
Hemoglobin SC
disease occurs when an individual inherits a hemoglobin S gene and a hemoglobin
C gene. The symptoms are similar to hemoglobin SS disease but often less
severe.
Globally,
hemoglobin SC disease is the second most common, but in Jordan, the second most
common is hemoglobin SB+ (beta) thalassemia.
Hemoglobin SB+
thalassemia affects the production of a specific component of hemoglobin. As a
result, the size of the red blood cell is smaller, but fortunately, symptoms
are less severe.
The last type is
hemoglobin SB 0 (beta-zero) thalassemia which also involves a disruption in
hemoglobin production. The symptoms for this type are similar to that of
hemoglobin SS; however, in certain cases, symptoms may be worse and are often
associated with a poorer prognosis.
Sickle cell symptoms
As mentioned previously, those with the sickle cell trait typically do
not have any symptoms. This is because the trait rarely leads to deformity in
the red blood cells.
On the other
hand, sickle cell disease has many associated symptoms and complications. One of
the main symptoms of sickle cell disease is sickle cell anemia. A healthy red
blood cell lives for up to 120 days, in those with sickle cell, the red blood
cell only lives for roughly 10–20 days. As a result of this high turnover rate,
the body cannot produce enough red blood cells.
The lack of red
blood cell production, in combination with sickle cell’s inherited inability to
properly bind to oxygen, many exacerbated symptoms associated with lack of
oxygen can occur. This includes fatigue, shortness of breath, low oxygen supply
to tissues, irregular heartbeats, and dizziness.
Red blood cells’
shape can also affect how the blood flows. Normally, the cell is smooth,
allowing it to pass through vessels and across other cells more easily. In
sickle cell disease, the irregular C shape of the cells can make movement
difficult and potentially cause them to bunch together. As a result, blood
clots can form and are responsible for many severe complications associated
with sickle cell disease.
Furthermore,
sickle cell disease can increase the risk of infection. The spleen is an organ
found in the abdomen which serves many roles, one of which is aiding in
immunity. This organ helps filter bacteria from the blood and helps produce
antibodies. In the early years of life, the irregularly shaped cell can block
the blood supply to the spleen and damage it, thus increasing susceptibility to
infection.
Blood clots
Almost all of the serious complications relate to that of clots being
formed. Clots can be painful or cause damage and are typically known as sickle
cell crises. They can be caused by different situations such as illness,
changes in temperature, stress, poor hydration, or high altitude.
Pain resulting
from a sickle cell crisis can be severe and last up to seven days on average.
One of the most common first signs of sickle cell disease is hand-foot
syndrome, which can occur in infancy. This syndrome is caused by clots blocking
the blood vessels that supply to the hands or feet. It will ultimately cause
swelling and potentially cause leg ulcers.
Blindness is
another complication of sickle cell disease, which can result due to blockages
in the eye.
Individuals with
sickle cell disease may also experience delayed growth. But it is ultimately
regained in adulthood.
More severe
complications of sickle cell disease that can affect the brain, heart, or lungs
exist as well. Clots in the brain can result in serious conditions such as
seizures, stroke, or even a coma.
Pain resulting from a sickle cell crisis can be severe and last up to seven days on average.
If an individual
experiences any symptoms relating to neurological complications, they are urged
to seek immediate treatment. These clots can also affect the heart, which can
cause heart attacks, heart failure, or abnormal heart rhythm.
Sickle cell
disease can seriously impact the lungs due to decreased blood flow, which can
cause damage and scarring known as pulmonary fibrosis, as well as high blood
pressure in the lungs known as pulmonary hypertension. These can be early signs
of a serious condition known as sickle chest syndrome.
Sickle chest
syndrome is a very severe crisis that causes severe chest pain and is
associated with hacking coughs, fever, shortness of breath, and low blood
oxygen levels. This is typically secondary to pneumonia or lung tissue death,
known as pulmonary infarction.
Those who have sickle chest
syndrome have a poorer long-term prognosis compared to those who do not.
Read more Health
Jordan News







